SAP Abap Webservice Soap
SAP Abap Webservice Soap Free Tutorial Download
SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP can be used both as a provider and a consumer of Web services. You can create, configure, publish, and consume services.
A Web service can be called in heterogeneous system landscapes and is not restricted to a particular host system. Output is determined by the system, based on the input parameters.
While Web services represent a technical concept, the service-oriented architecture enables you to design a complete solution for any business application.
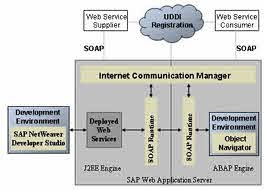
The Web Services Framework comprises the development environment of SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP, the Enterprise Services Repository tools to support UDDI registration to the Services Registry, and an interoperable SOAP runtime environment. For more information, see Working with a Services Registry.
SOAP requests are processed using the Internet Communication Framework. The http protocol of the Internet Communication Framework is used for communication between the consumer and the provider.
Web Service Standards
SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI are the core standards for all Web service approaches. SOAP provides standards for a general, application-independent format for XML messages. XML messages can be exchanged between the communication partners using different transport protocols. WSDL adds on the application-related component. Using this language, you can describe the interface for actual Web services. The latter consist of names of operations as well as input and output messages. At runtime, they are packed into SOAP messages and transmitted. UDDI provides the additional option of being able to publish and look for Web services.
The standards supported by SAP are described in the section Supported Standards.
Eclipse-Based ABAP Development Tools
Note that you can also develop Web services and integration scenarios with the Eclipse-based ABAP Development Tools. For more information, choose Help in the ABAP Development Tools to find the Eclipse Help Book about ABAP Web Services.
-
If the AS ABAP functions as a service provider, a service interface is created for the implemented function. This represents the Web service for the user. Based on this interface, the service is configured and can be called at runtime.
-
If the AS ABAP has the function of a service consumer, it is possible to generate a proxy – in just a few steps – using a WSDL document. The service can be called from a program.
-
Working with Integration Scenarios.
You can define entire integration scenarios that can be easily configured.
-
Configuring the Web Service Runtime
Both the service consumer and the service provider must be configured at runtime.
-
Working with a Services Registry
You can store released Web services in the Services Registry. Web services can be searched for and published in Services Registries.
-
Managing the Web Service Runtime
To be able to use Web Services with Web Services Reliable Messaging, you must have the Web service runtime configured.
More information: Configuring the Web Service Runtime.
In the AS ABAP, different tools for monitoring the Web service runtime are available.
More information: Monitoring the Web Service Runtime.
-
Secure Runtime Configuration with the SOA Manager
To configure special security settings, you must configure security settings in the systems of the consumers and providers that communicate with one another.
More information: Working with the SOA Manager
Download SAP Abap Webservice Soap Free
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1X1v13bGZBUYEzltRKgFdhAHaJ0ciaUuQ/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Mex6GzreH22X7iYcQmMB-tRLfywGJuo9/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1dEwtGz5I6fWVJr-UGx3JDxqaigTGmY2B/view?usp=sharing
https://uptobox.com/jl2g0aelphjh